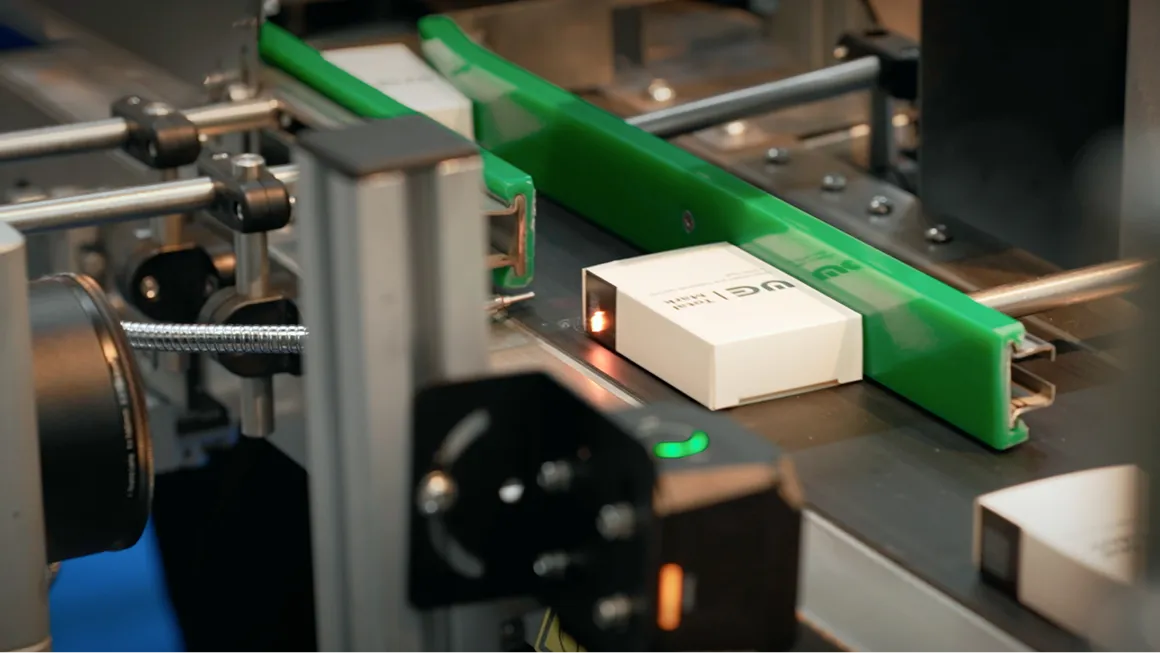
The Central African Republic is set to introduce innovative Digital Track and Trace technology in partnership with DigitalGate, SARL, before the end of the year. With this change, the government aims to enhance transparency, improve supply chain management, and strengthen public safety.
But what exactly is Digital Track and Trace, what benefits does it have, and how it will affect businesses in the country?
Let’s break it down.
What is Digital Track and Trace?
Each DataMatrix code is scanned at every stage, and the product manufacturing and movement information is sent to the system — when it is produced, transferred from the manufacturer to the distributor, from the distributor to the retailer, and finally sold to the customer. Such codes are unique and protected against counterfeiting, which allows verifying the authenticity of the products.
Are DataMatrix Codes and QR Codes the Same Thing?
While they are often confused with QR codes, DataMatrix codes are different. They consist of vertical and horizontal lines that form the finder pattern in the “L” shape.
The overlap in the bottom left corner indicates the starting pixel from which the code is read. These codes can be either square or rectangular and contain any information coded in the form of letters, numbers, and symbols.
Here’s what a DataMatrix code looks like:
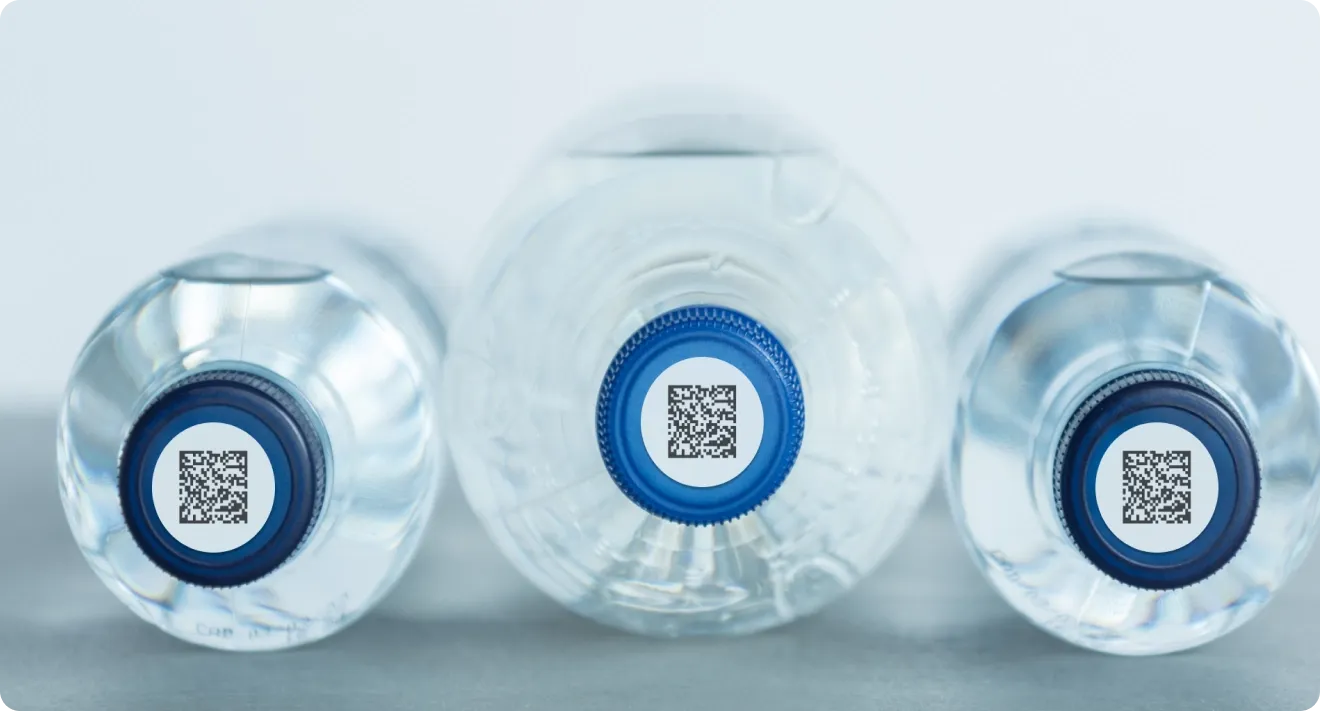

Unlike QR codes, DataMatrix codes have their own error correction mechanism that helps read them even if they are damaged.
The Purpose of Digital Track and Trace
The primary goal of Digital Track and Trace is to protect citizens of the Central African Republic against counterfeit, unsafe, and substandard products. This technology offers a wide range of benefits for the country that extend beyond just safety, impacting governments, businesses, and everyday shoppers alike.
Improving Government Efficiency
The government of the Central African Republic can more effectively fight illicit trade, contraband, and counterfeit goods that can harm public health by accurately tracking products through the supply chain. This, in turn, helps protect the citizens’ health by enabling swift detection and recall of dangerous products. Moreover, real-time market data access allows the government to respond quickly to changes and emerging trends, giving businesses within the country more room for development.
Supporting Local Businesses and Fair Competition
By eliminating counterfeit products, businesses can preserve their brand integrity and maintain consumer trust.
The system enables efficient product recalls, protecting both consumers and a company’s reputation. Real-time tracking improves inventory management, while seamless integration with import and export processes simplifies cross-border trade.
Additionally, fair competition is encouraged by promoting efficient tax compliance, leveling the playing field for all market participants.
Providing Greater Safety and Convenience to Citizens
A dedicated mobile application empowers shoppers to confirm product authenticity, protecting their health and rights. Each product carries a unique, secure code that guarantees genuineness and helps prevent fraud.
Access to verified purchase records simplifies returns and warranty claims, enhancing overall customer experience.
How Does Digital Track and Trace Work?
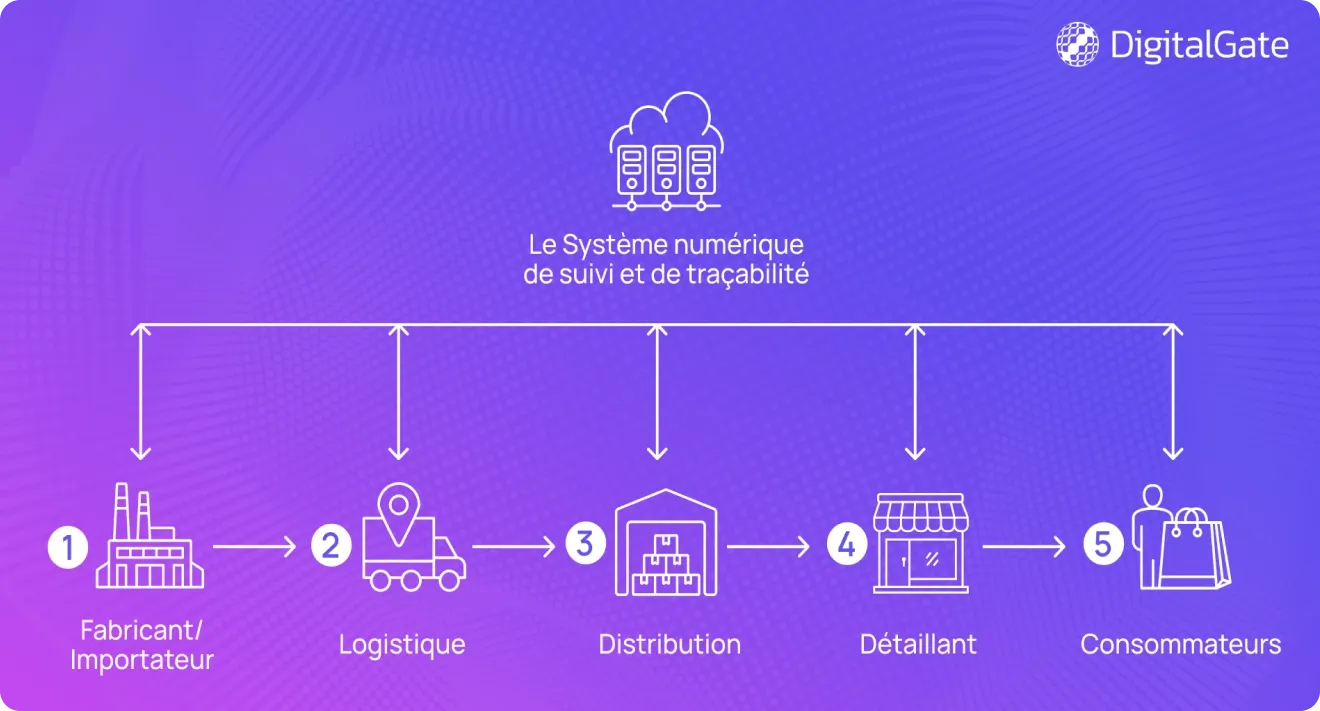
- The manufacturer or importer applies DataMatrix codes to the product packaging before shipping the items to the distributor.
- Upon receiving the shipment, the distributor scans the batch of products and forwards them to retail stores and supermarkets.
- When stores receive new product batches, staff scan the packaging codes and sell only verified legal products at the checkout.
- At the point of sale, a 2D scanner reads the DataMatrix code, which is then recorded as removed from the product inventory.
- Customers can use a mobile app to scan the DataMatrix code and verify the product’s authenticity and origin.
When Does Digital Track and Trace Launch in CAR?
In the Central African Republic, Digital Track and Trace is scheduled to launch in pilot mode for five product categories later this year. At that stage, selected businesses will participate to test the system.
The technology will be fully implemented on January 1, 2026. Starting that day, registration in the system will be mandatory, and sanctions will be enforced against businesses attempting to bypass the process.
Therefore, it’s important for businesses to get familiar with the system and understand how it works in advance.
What Track and Trace Equipment Do Participants Need?
To implement the technology, manufacturers and importers will have to apply DataMatrix codes to products. Special equipment is required to do that, such as:
- Laser goods marking equipment (good for mid- to large-sized businesses);
- Inkjet DataMatrix printers (less expensive than the laser systems, ideal for small- to medium-sized businesses);
- DataMatrix sticker printers (the least expensive and complicated way to apply DataMatrix codes to products, suits micro- to small-sized businesses best).
Necessary support and education will be provided to help manufacturers and importers adapt to all changes.
What other equipment is required?
All participants — manufacturers, importers, distributors, and retailers – will also need such technology as:
- DataMatrix code scanners to get instant access to product information at every stage of the supply chain;
- Mobile application that can replace traditional scanners, provide the option to file complaints and get additional information.
Let’s Sum It Up
The implementation of Digital Track and Trace is a big step forward for the Central African Republic on its digital transformation journey, as it will lead to many positive changes for all stakeholders — the government, businesses, and consumers.
The technology will help achieve market transparency, improve the investment climate, bring many businesses out of the shadow, tackle illicit trade, and protect brands and consumers from counterfeiting.
